本文讲解如何通过 Contract Size Check 判断调用者身份。
作者:小白, 慢雾安全团队
背景概述
在第一期文章中我们提过防止重入攻击的多种方式,其中一种是通过检查调用者身份并禁止合约调用来防止重入攻击。这期文章我们就来了解如何通过 Contract Size Check 判断调用者身份。
前置知识
众所周知,合约是由代码编写的,所以部署后的合约地址肯定有相应的字节码,而 EOA 地址是没有字节码的,所以我们只需要检查调用者地址是否有字节码就可以判断调用者是否为合约。这里需要使用 Solidity 内联汇编中的 extcodesize() 函数。下面我们还是通过实例来看看这个函数的实际效果。
代码示例
首先,我们用一个代码示例来了解 extcodesize() 的作用。
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MITpragma solidity ^0.8.20;
contract CheckCodeSize { function Size(address account) public view returns (uint256) { uint size; assembly { size := extcodesize(account) } return size; }}我们在 Remix 上部署后,调用 Size() 并传入 Deployer 的 EOA 地址(0x787···cabaB),发现返回 0。
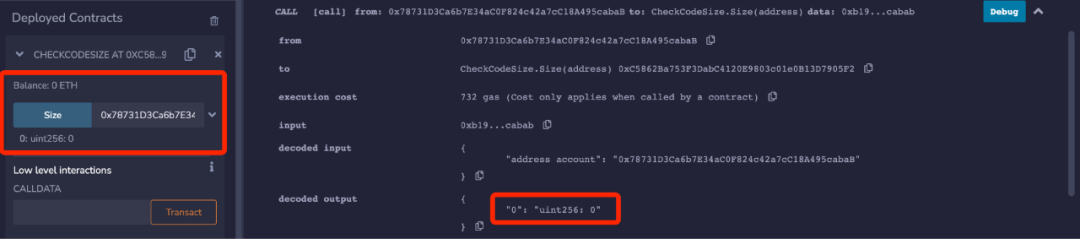
我们再次调用 Size() 并传入合约自身地址(0xC58···905F2),返回 348。

综上可知,当 account 为 EOA 地址时,extcodesize() 会返回 0 ,当 account 为合约地址时,extcodesize() 会返回合约部署后的字节码大小。到这里,相信大家不难想到可以通过调用 extcodesize() 并看其返回值是否为 0 来判断该地址是 EOA 还是部署后的合约。诶,漏洞就这么写出来了。
漏洞示例
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MITpragma solidity ^0.8.20;
contract Target { function isContract(address account) public view returns (bool) { uint size; assembly { size := extcodesize(account) } return size > 0; }
bool public pwned = false;
function protected() external { require(!isContract(msg.sender), "no contract allowed"); pwned = true; }}漏洞分析
可以看到,isContract() 判断 account 字节码是否为 0 并返回 bool 类型的值。protected() 则会根据 isContract() 的返回值来修改 pwned 的状态。但是这里忽略了一个点,即合约部署时,constructor 函数中的代码逻辑会跟随部署合约的交易一起发送给矿工打包上链。由于此时合约部署的操作还没有完成,所以合约地址还没有存入相应的字节码,这时在 consturctor 函数中调用 extcodesize() 检查合约地址的字节码就会返回 0 。下面我们来看正常调用的情况下会返回什么:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MITpragma solidity ^0.8.20;
contract FailedAttack { function pwn(address _target) external { Target(_target).protected(); }}调用 pwn() 并将合约地址 0x058···4c899 传入会被 revert,这里说明合约部署后调用 protected() 会无法通过 require(!isContract(msg.sender) 检查。
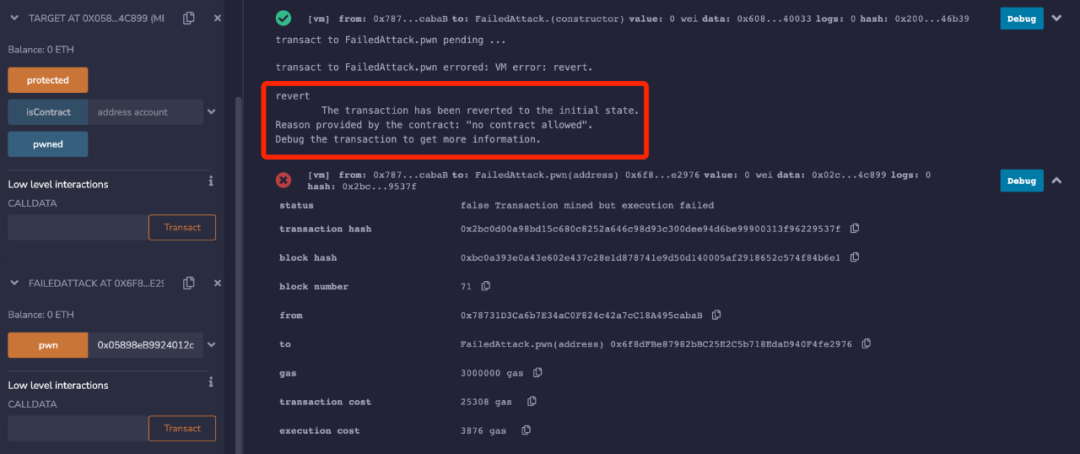
攻击合约
下面我们将调用逻辑放在 constructor 函数中再次尝试:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MITpragma solidity ^0.8.20;
contract Hack { bool public isContract; address public addr;
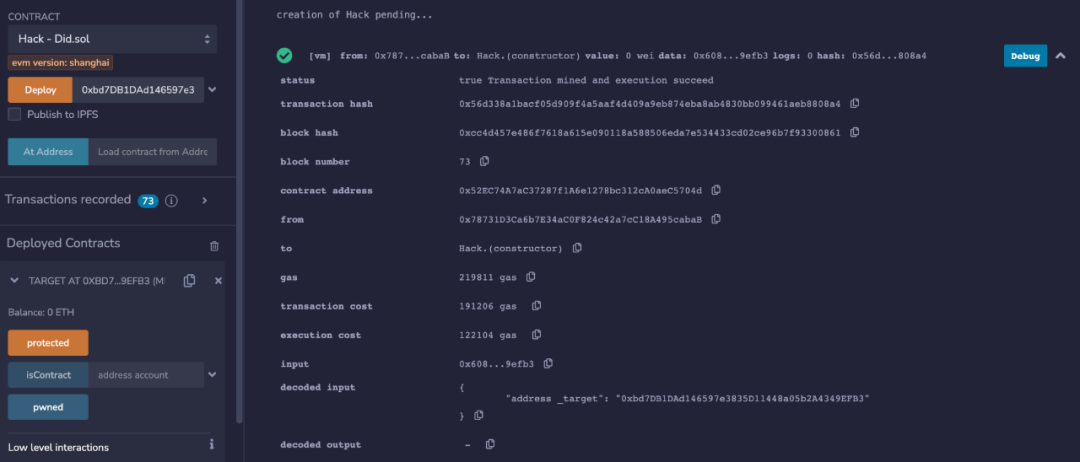
// When contract is being created, code size (extcodesize) is 0. // This will bypass the isContract() check constructor(address _target) { isContract = Target(_target).isContract(address(this)); addr = address(this); // This will work Target(_target).protected(); }}部署 Hack 合约时传入 0xbd7···9EFB3 合约地址,发现成功绕过了 require(!isContract(msg.sender) 检查,而且成功修改了 pwned 的状态。
修复建议
作为开发者
使用 extcodesize() 判断地址是否为 EOA 地址并不准确,在实际开发中最稳妥的判断调用者身份的方式还是通过 tx.origin 来判断。类似下面这样:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MITpragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract EOAChecker { function isEOA() external pure returns (bool) { return msg.sender == tx.origin; }}由于 tx.origin 只可能是 EOA 地址,我们只需要判断上层调用者的 msg.sender 是否与 tx.origin 为同一地址就可以。以刚刚的漏洞代码为例,我们只需要稍加修改就可以修复漏洞。
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MITpragma solidity ^0.8.20;
contract Target { function isContract() public view returns (bool) { return (msg.sender == tx.origin); }
bool public pwned = false;
function protected() external { require(isContract(), "no contract allowed"); pwned = true; }}此时部署下面这个 Hack 合约再进行攻击,就会被 revert 并返回 "no contract allowed"。
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MITpragma solidity ^0.8.20;
contract Hack { address public addr;
constructor(address _target) { Target(_target).protected(); }}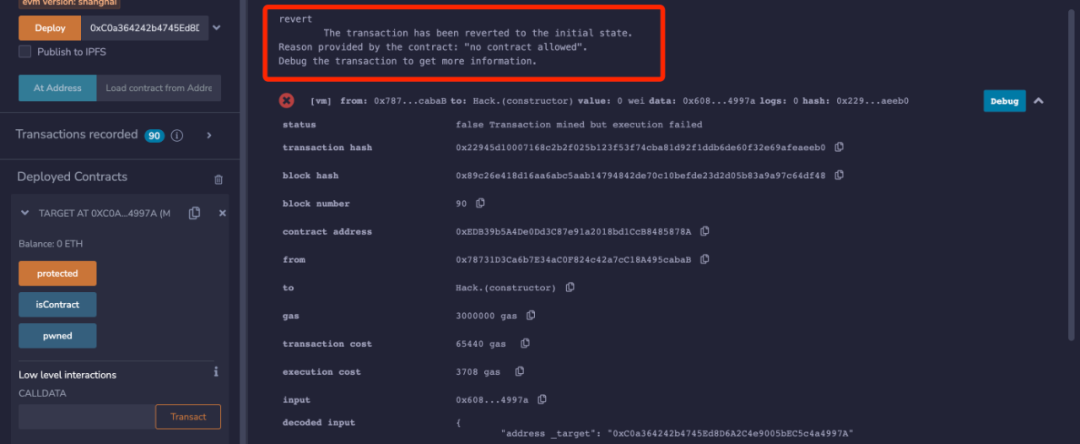
作为审计者
在审计过程中,如果遇到限制合约地址调用的逻辑,应当结合实际业务逻辑判断该检查是否严谨以及是否存在被绕过的可能。
免责声明:作为区块链信息平台,本站所发布文章仅代表作者及嘉宾个人观点,与 Web3Caff 立场无关。本文内容仅用于信息分享,均不构成任何投资建议及要约,并请您遵守所在国家或地区的相关法律法规。