ChainLink 采用了分布式价格预言机的设计来为用户提供服务
作者:ZAN Team
封面:Chainlink
分布式价格预言机
当消费者请求预言机服务时,预言机可能会因为各种各样的原因无法及时响应,从而造成单点故障。因此,ChainLink 采用了分布式价格预言机的设计来为用户提供服务。例如,一个提供 BTC 美元价格的服务,聚合了 31 个价格预言机为用户提供服务。

该聚合器的合约源码可以在 Etherscan 上查看:https://etherscan.io/address/0xae74faa92cb67a95ebcab07358bc222e33a34da7#readContract
其中,通过调用合约中的 transmitters 方法即可查看该聚合器包含的所有链下预言机。
function transmitters() external view returns(address[] memory){ return s_transmitters; }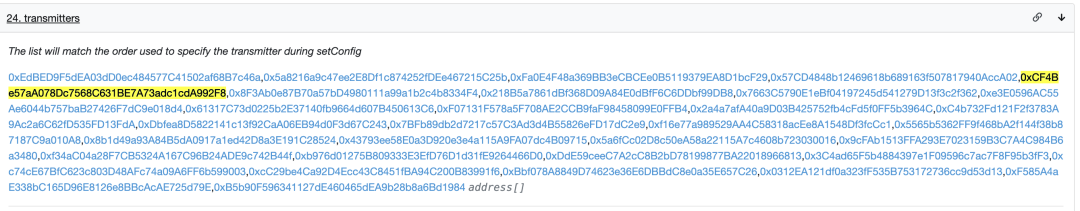
每一个链下预言机可以通过调用 transmit 方法来提供价格数据,以响应聚合器中用户的请求。这些链下预言机是一些 EOA 账户,他们不仅为 BTC/USD 聚合器提供价格数据,还可能为其他聚合器提供价格数据,例如 ETH/USD。
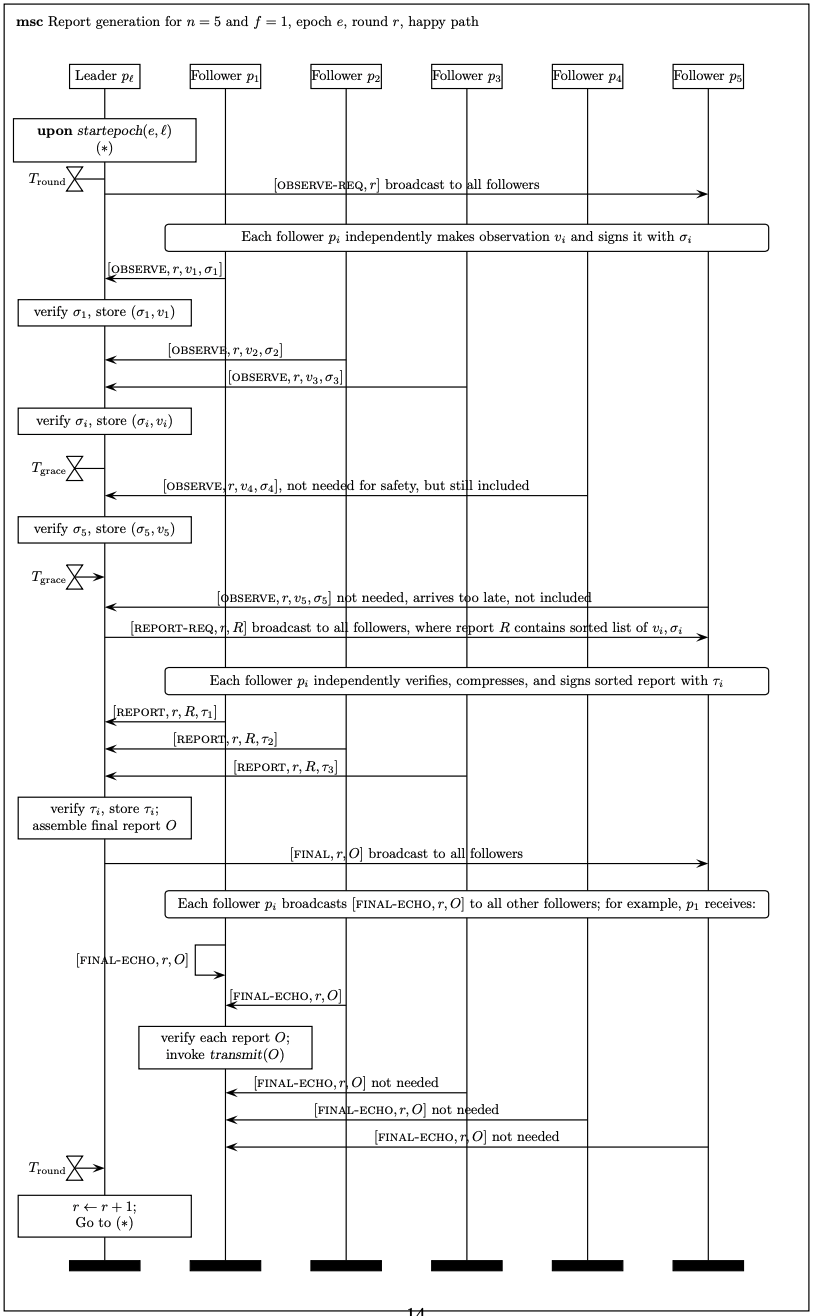
链上合约:
struct Transmission { int192 answer; // 192 bits ought to be enough for anyone uint64 timestamp; }
enum Role { // No oracle role has been set for address a Unset, // Signing address for the s_oracles[a].index'th oracle. I.e., report // signatures from this oracle should ecrecover back to address a. Signer, // Transmission address for the s_oracles[a].index'th oracle. I.e., if a // report is received by OffchainAggregator.transmit in which msg.sender is // a, it is attributed to the s_oracles[a].index'th oracle. Transmitter }
struct Oracle { uint8 index; // Index of oracle in s_signers/s_transmitters Role role; // Role of the address which mapped to this struct }
struct HotVars { // Provides 128 bits of security against 2nd pre-image attacks, but only // 64 bits against collisions. This is acceptable, since a malicious owner has // easier way of messing up the protocol than to find hash collisions. bytes16 latestConfigDigest; // 提供抗弱碰撞性摘要 uint40 latestEpochAndRound; // 32 most sig bits for epoch, 8 least sig bits for round(round 是 leader 的标志) uint8 threshold; // 敌手数量 uint32 latestAggregatorRoundId; // 链上最新的 roundId,链下 reporting 不会使用 }
struct ReportData { HotVars hotVars; // Only read from storage once bytes observers; // ith element is the index of the ith observer int192[] observations; // ith element is the ith observation bytes vs; // jth element is the v component of the jth signature bytes32 rawReportContext;}
function transmit( // NOTE: If these parameters are changed, expectedMsgDataLength and/or // TRANSMIT_MSGDATA_CONSTANT_LENGTH_COMPONENT need to be changed accordingly bytes calldata _report, bytes32[] calldata _rs, bytes32[] calldata _ss, bytes32 _rawVs // signatures ) external { uint256 initialGas = gasleft(); // This line must come first // Make sure the transmit message-length matches the inputs. require(msg.data.length == expectedMsgDataLength(_report, _rs, _ss), "transmit message too long"); ReportData memory r; { r.hotVars = s_hotVars; // 读取上一轮的相关参数
bytes32 rawObservers; (r.rawReportContext, rawObservers, r.observations) = abi.decode( _report, (bytes32, bytes32, int192[]) );
// rawReportContext consists of: // 11-byte zero padding // 16-byte configDigest // 4-byte epoch // 1-byte round bytes16 configDigest = bytes16(r.rawReportContext << 88); require( r.hotVars.latestConfigDigest == configDigest, "configDigest mismatch" ); // 检查是否存在 hash 碰撞
uint40 epochAndRound = uint40(uint256(r.rawReportContext)); // 截取 uint256 的后 40 位 // direct numerical comparison works here, because // // ((e,r) <= (e',r')) implies (epochAndRound <= epochAndRound') // // because alphabetic ordering implies e <= e', and if e = e', then r<=r', // so e*256+r <= e'*256+r', because r, r' < 256 require(r.hotVars.latestEpochAndRound < epochAndRound, "stale report"); require(_rs.length > r.hotVars.threshold, "not enough signatures"); // 检查签名数量 require(_rs.length <= maxNumOracles, "too many signatures"); require(_ss.length == _rs.length, "signatures out of registration"); require(r.observations.length <= maxNumOracles, "num observations out of bounds"); require(r.observations.length > 2 * r.hotVars.threshold, "too few values to trust median"); // Copy signature parities in bytes32 _rawVs to bytes r.v r.vs = new bytes(_rs.length); for (uint8 i = 0; i < _rs.length; i++) { r.vs[i] = _rawVs[i]; }
// Copy observer identities in bytes32 rawObservers to bytes r.observers r.observers = new bytes(r.observations.length); bool[maxNumOracles] memory seen; for (uint8 i = 0; i < r.observations.length; i++) { uint8 observerIdx = uint8(rawObservers[i]); require(!seen[observerIdx], "observer index repeated"); seen[observerIdx] = true; r.observers[i] = rawObservers[i]; } Oracle memory transmitter = s_oracles[msg.sender]; require( // Check that sender is authorized to report transmitter.role == Role.Transmitter && msg.sender == s_transmitters[transmitter.index], "unauthorized transmitter" ); // record epochAndRound here, so that we don't have to carry the local // variable in transmit. The change is reverted if something fails later. r.hotVars.latestEpochAndRound = epochAndRound; }
{ // Verify signatures attached to report bytes32 h = keccak256(_report); bool[maxNumOracles] memory signed; Oracle memory o; for (uint i = 0; i < _rs.length; i++) { // v 取出来的值或者是 00 或 01。要使用时,我们先要将其转为整型,再加上 27,所以我们将得到 27 或 28。在调用函数时 v 将填入 27 或 28 address signer = ecrecover(h, uint8(r.vs[i])+27, _rs[i], _ss[i]); o = s_oracles[signer]; require(o.role == Role.Signer, "address not authorized to sign"); require(!signed[o.index], "non-unique signature"); signed[o.index] = true; } } { // Check the report contents, and record the result for (uint i = 0; i < r.observations.length - 1; i++) { bool inOrder = r.observations[i] <= r.observations[i+1]; require(inOrder, "observations not sorted"); } int192 median = r.observations[r.observations.length/2]; require(minAnswer <= median && median <= maxAnswer, "median is out of min-max range"); r.hotVars.latestAggregatorRoundId++; s_transmissions[r.hotVars.latestAggregatorRoundId] = Transmission(median, uint64(block.timestamp)); emit NewTransmission( r.hotVars.latestAggregatorRoundId, median, msg.sender, r.observations, r.observers, r.rawReportContext ); // Emit these for backwards compatability with offchain consumers // that only support legacy events emit NewRound( r.hotVars.latestAggregatorRoundId, address(0x0), // use zero address since we don't have anybody "starting" the round here block.timestamp ); emit AnswerUpdated( median, r.hotVars.latestAggregatorRoundId, block.timestamp ); validateAnswer(r.hotVars.latestAggregatorRoundId, median); } s_hotVars = r.hotVars; assert(initialGas < maxUint32); reimburseAndRewardOracles(uint32(initialGas), r.observers); }1. 首先,读取当前合约状态,并进行一系列的检查:

2. 这些都通过后,可以进行一些准备工作了:

3. 接下来是使用 ecrecover() 对对每一个签名数据进行验签,校验 hash 值是对 _report 做的 hash。同时还要检查签名者的角色是否是 Signer,且要检查签名的重复性。
4. 最后,检查观察值是否按照顺序排列好。再从排好顺序的观察值中选取中位数 median,并确保 median 不超过上下两个阈值。一切都没问题后,在 s_transmissions 中记录下本次预言机的 answer。此外,还要对 answer 进行校验:
function validateAnswer(uint32 _aggregatorRoundId, int256 _answer) private { ValidatorConfig memory vc = s_validatorConfig; if (address(vc.validator) == address(0)) { return; }
uint32 prevAggregatorRoundId = _aggregatorRoundId - 1; int256 prevAggregatorRoundAnswer = s_transmissions[prevAggregatorRoundId].answer; require( callWithExactGasEvenIfTargetIsNoContract( vc.gasLimit, address(vc.validator), abi.encodeWithSignature( "validate(uint256,int256,uint256,int256)", uint256(prevAggregatorRoundId), prevAggregatorRoundAnswer, uint256(_aggregatorRoundId), _answer ) ), "insufficient gas" ); }这里经过一系列(中间有 Proxy 合约)的 call 最终调用了 UniswapAnchoredView 合约 (Compound 使用的价格预言机) 的 validate 方法:
function validate(uint256/* previousRoundId */, int256 /* previousAnswer */, uint256 /* currentRoundId */, int256 currentAnswer) external override returns (bool valid) {
// NOTE: We don't do any access control on msg.sender here. The access control is done in getTokenConfigByReporter, // which will REVERT if an unauthorized address is passed. TokenConfig memory config = getTokenConfigByReporter(msg.sender); // 获取预言机 report 中的价格 uint256 reportedPrice = convertReportedPrice(config, currentAnswer); // 获取 UniswapV2 价格预言机计算得到的价格 uint256 anchorPrice = calculateAnchorPriceFromEthPrice(config);
PriceData memory priceData = prices[config.symbolHash]; if (priceData.failoverActive) { require(anchorPrice < 2**248, "Anchor price too large"); prices[config.symbolHash].price = uint248(anchorPrice); emit PriceUpdated(config.symbolHash, anchorPrice); } else if (isWithinAnchor(reportedPrice, anchorPrice)) { require(reportedPrice < 2**248, "Reported price too large"); prices[config.symbolHash].price = uint248(reportedPrice); emit PriceUpdated(config.symbolHash, reportedPrice); valid = true; } else { emit PriceGuarded(config.symbolHash, reportedPrice, anchorPrice); } }关键是比较了两边预言机给的价格的偏差是否在一个范围内:
function isWithinAnchor(uint reporterPrice, uint anchorPrice) internal view returns (bool) { if (reporterPrice > 0) { uint anchorRatio = mul(anchorPrice, 100e16) / reporterPrice; return anchorRatio <= upperBoundAnchorRatio && anchorRatio >= lowerBoundAnchorRatio; } return false; }Feed Registry
前面的使用方式虽然已经很简单,但如果需要不同 token 的价格就得对每个 token 执行 setPriceFeed,治理成本其实有点高,对某些场景来说就不太灵活。这时候,就可以考虑使用 Feed Registry 的方式来接入。
Feed Registry 可以简单理解为 PriceFeeds 的聚合器,已经聚合了多个 priceFeed,有了它,使用者就无需自己去设置 priceFeed 了,可直接通过 Feed Registry 读取价格数据,如下图:
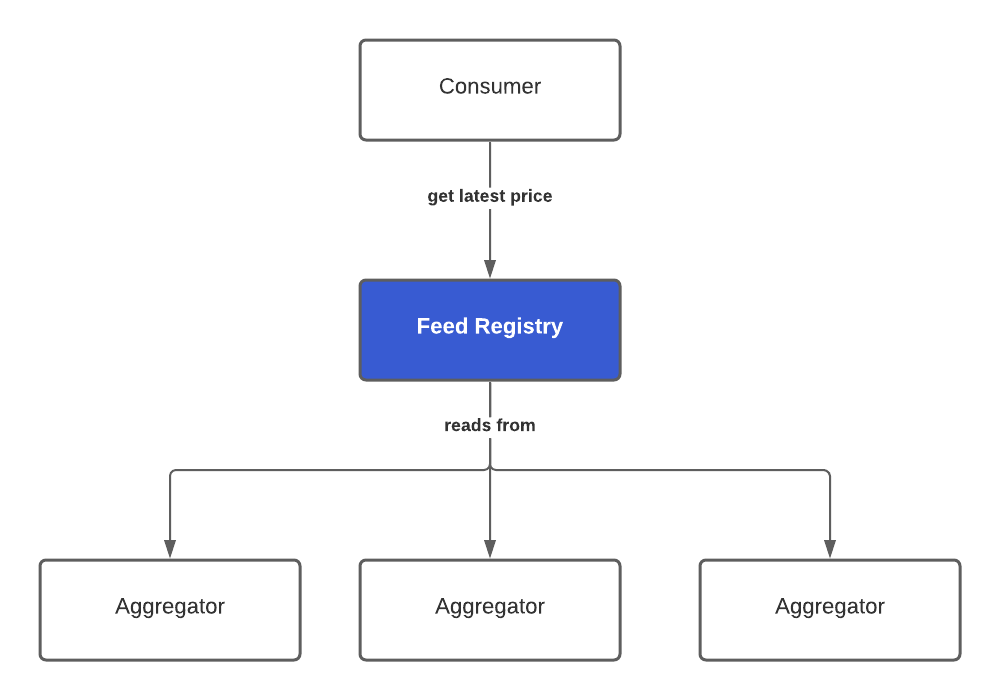
喂价机制
首先,Price Feed 的价格是通过多个层级的数据聚合得到的。实际上有三个数据聚合层:数据源聚合、节点运营商聚合、预言机网络聚合。
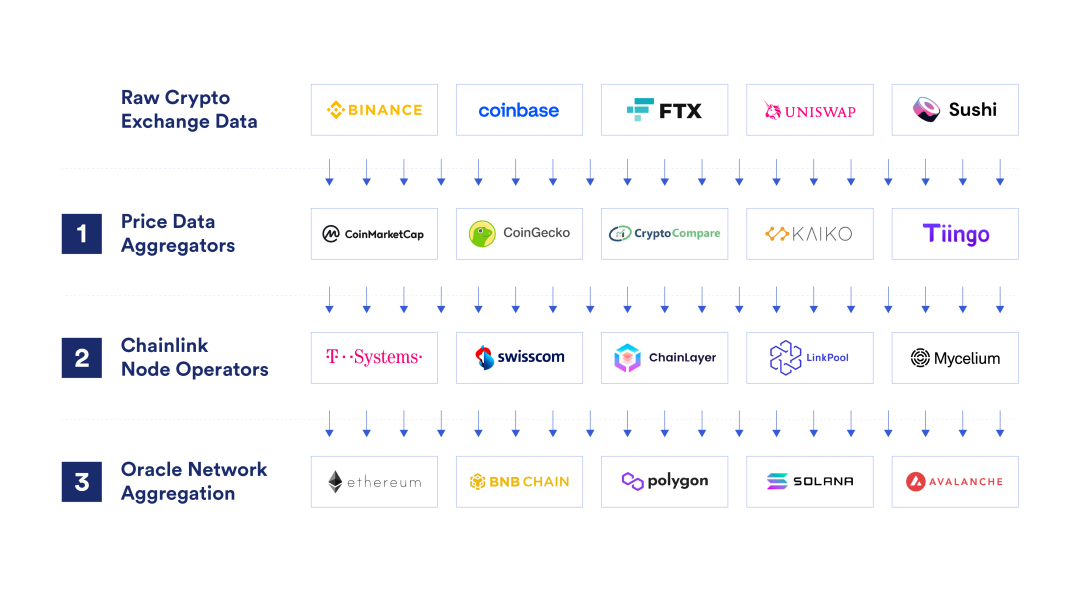
最原始的价格数据主要来源于币安、火币、Coinbase 等中心化交易平台,以及 Uniswap、Sushi 等去中心化交易平台。存在一些专门做数据聚合的服务商(比如 amberdata、CoinGecko),会从这些交易平台收集原始的价格数据,并对这些数据源进行加工整合,比如根据交易量、流动性和时差等进行加权计算。
这就是第一个层面的聚合,对数据源的聚合。拥有可靠的价格数据源的关键是要有全面的市场覆盖,才能保证一个价格点能代表所有交易环境的精确聚合,而不是单个交易所或少数交易所的价格,以防止数据被人为操纵和出现价格偏差。
第二层则是 Chainlink Node Operators 所做的聚合。每个 Chainlink Node Operator 主要负责运行用于在区块链上获取和广播外部市场数据的 Chainlink 核心软件。Node Operators 会从多个独立的数据聚合服务商获取价格数据,并获取它们之间的中值,剔除掉异常值和 API 停机时间。
最后一层则是整个预言机网络的聚合,其聚合的方式有多种,但最常见的聚合方式是当响应节点数量达到预设值时对数据取中值。比如总共有 31 个节点,预设值为 21,即收到了 21 个节点的响应后,就取这些节点的价格数据的中值作为最终的价格。不过,并非每一轮的价格结果都会更新到链上,只有满足两个触发参数之一的时候才会更新:偏差阈值(Deviation Threshold)和心跳阈值(Heartbeat Threshold)。而且,不同 PriceFeed 的这两个参数的值可能会不一样。
总而言之,Chainlink 价格预言机接入方便,且安全性还是比较高的,但因为其价格更新机制存在偏差阈值,导致价格更新比较慢,短则几分钟或几十分钟更新一次,长则可能达 24 小时才更新一次,因此,一般只适用于对价格更新不太敏感的应用。这也是 Chainlink 价格预言机的局限性,并无法适用所有场景的应用。
免责声明:作为区块链信息平台,本站所发布文章仅代表作者及嘉宾个人观点,与 Web3Caff 立场无关。本文内容仅用于信息分享,均不构成任何投资建议及要约,并请您遵守所在国家或地区的相关法律法规。




















